node js application - Node.js First Application - node js - node js tutorial
Related nodejs article tags - node js - node js tutorial - node js examples
What is Node.js?
- Node.js is a cross-platform runtime environment and library for running JavaScript applications outside the browser.
- It is used for creating server-side and networking web applications.
- It is open source and free to use. It can be downloaded from this link https://nodejs.org/en/
Related nodejs article tags - node js - node js tutorial - node js examples
Node.js benefits
- Node.js dependency on JavaScript leads to its fame because, JavaScript is widely utilized by most programmers to create client side scripting code in the browser.
- Node’s simplicity with minimal exposure of code complexity makes it as preferable option.
- Existing library code can be easily selected, installed and used.
- Installation and configurations are very simple and performed within few minutes of time.
Related nodejs article tags - node js - node js tutorial - node js examples
Node.js Gateway
- node.js offers elastic asynchronous I/O operations through its javascript features.
- The major advantage of node.js is that it process the threads in the background at the server.
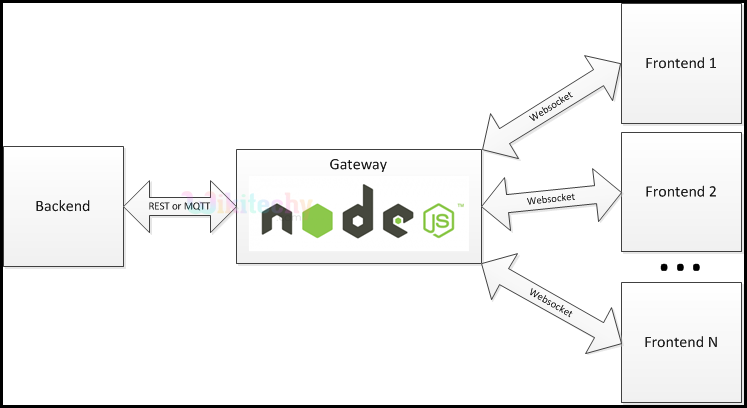
- As per above figure, consider various file requests from widespread front end devices on a server with node.js implementation.
- There is a requirement for a callback function to be executed when the file operation has finished.
- Following steps are applied to achieve this:
- Data request is passed via web sockets to node.js.
- Node.js is used as a gateway to handle these requests.
- It then interacts with the backend via an interface (REST or MQTT) and returns back the data.
First Application in nodejs
- Let us discuss the components of a Node.js application, before creating an actual "Hello, Wikitechy!" application using Node.js A Node.js application consists of three important components :
- Import required modules − We use the require directive to load Node.js modules.
- Create server − A server which will listen to client's requests related to Apache HTTP Server.
- Read request and return response − The server created in an earlier step will read the HTTP request made by the client which can be a browser or a console and return the response.

Learn Node js - node js Tutorial - node.js first application - - node - Node js Examples
Creating Node.js Application
Learn Node js - node js Tutorial - process of node.js first application - - node - Node js Examples
Step 1 - Import Required Module
- We use the require directive to load the http module and store the returned HTTP example into an http variable as follows
var http = require("http");
Step 2 - Create Server
- We use the created http instance and call http.createServer()method to create a server instance and then we bind it at port 8081 using the listen method associated with the server instance.
- Pass it a function with parameters request and response.
- Write the sample implementation to always return "Hello Wikitechy".
http.createServer(function (request, response) {
// Send the HTTP header
// HTTP Status: 200 : OK
// Content Type: text/plain
response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'});
// Send the response body as "Hello Wikitechy"
response.end('Hello Wikitechy\n');
}).listen(8081);
// Console will print the message
console.log('Server running at http://127.0.0.1:8081/');
- The above code is enough to create an HTTP server which listens, i.e., waits for a request over 8081 port on the local machine.
Step 3 - Testing Request & Response
- Put step 1 and 2 together in a file called main.js and start our HTTP server as shown below
Related nodejs article tags - node js - node js tutorial - node js examples
main.js
var http = require("http");
http.createServer(function (request, response) {
// Send the HTTP header
// HTTP Status: 200 : OK
// Content Type: text/plain
response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'});
// Send the response body as "Hello Wikitechy"
response.end('Hello Wikitechy\n');
}).listen(8081);
// Console will print the message
console.log('Server running at http://127.0.0.1:8081/');
- Now execute the main.js to start the server as follows
$ node main.js
Related nodejs article tags - node js - node js tutorial - node js examples
Output
- Server has started.
Server running at http://127.0.0.1:8081/
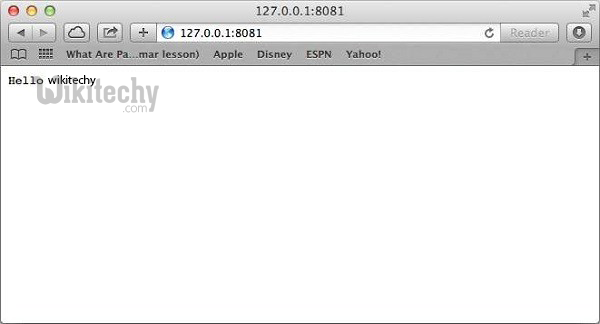
Make a Request to the Node.js Server
- Open http://127.0.0.1:8081/ in any browser and observe the following result.
Learn Node js - node js Tutorial - node.js first application - - node - Node js Examples
- Your first HTTP server up and running which is responding to all the HTTP requests at port 8081.
