How Market Orders Differ From Limit Orders in Spot Trading
Spot trading involves the immediate exchange of financial assets at current market prices. It allows traders to instantly buy or sell cryptocurrencies, stocks, or other instruments without deferred settlement. Order types play a critical role in shaping execution quality, controlling risk exposure, and influencing overall trading outcomes. Understanding these order types is fundamental for anyone seeking consistent results in spot markets. This article explores market and limit orders, their differences, and strategic applications. Insights include practical guidance for traders, with examples, and real-world applications in a professional trading environment.
Core Mechanics of Spot Trading Orders
Spot markets operate through order books where buyers and sellers submit their intentions. These orders collectively establish bid and ask levels, reflecting market sentiment at any given moment. Matching engines continuously scan the order book to pair compatible buy and sell instructions, finalising trades efficiently. Traders who consume existing orders are price takers, while those placing orders into the book provide liquidity as price makers. A strong grasp of execution mechanics ensures traders select the most suitable order type for their goals. It also clarifies how market conditions, such as liquidity depth and volatility, affect execution outcomes and overall trading efficiency.
Market Orders Explained in Depth
A market order is an instruction to buy or sell instantly at the best available price. When executed, it consumes existing liquidity from the order book, prioritising speed over price precision. Market orders are commonly used when immediate execution is necessary, such as entering a trending position or exiting during sudden volatility. Their advantages include guaranteed execution and suitability for high‑liquidity pairs, making them ideal for urgent transactions. However, traders have no control over the final execution price, and during volatile periods, slippage may increase significantly. According to CoinMarketCap, a leading crypto data provider with billions in market metrics annually, Spot Trading on Zoomex.com shows how traders can leverage such order types efficiently.
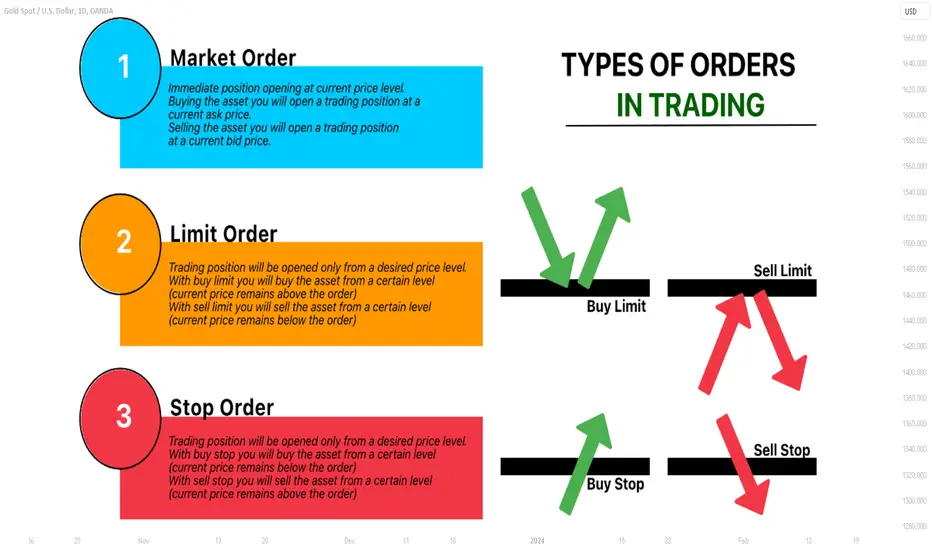
Limit Orders Explained in Depth
Limit orders instruct the market to execute a trade only at a specified price or better. Unlike market orders, they add liquidity to the order book rather than consuming it. Buy limit orders are placed below the current market price, whereas sell limit orders are set above it. Limit orders may remain open until the price condition is met or the order expires, which introduces time considerations. They are strategically advantageous when traders aim to control prices or enter or exit positions under defined conditions. However, limit orders risk non-execution if the market never reaches the desired price. By carefully managing limit orders, traders can optimise execution costs, contribute to order-book depth, and control price exposure.
Impact on Price Discovery and Market Liquidity
Market and limit orders influence short-term price dynamics differently. Market orders, by immediately consuming liquidity, often cause temporary price movements, particularly in low-depth markets. Limit orders stabilise price ranges by offering visible bids and asks, enhancing transparency. They contribute to the depth of the order book, allowing other participants to evaluate supply and demand more accurately. Liquidity levels directly affect execution quality, as thin markets amplify slippage for market orders and prolong waiting times for limit orders. During periods of high volatility or reduced liquidity, understanding how these orders interact with the market helps make more informed, controlled trading decisions.
Risk Management and Execution Strategy Considerations
Choosing the right order type is critical for managing trading risk. Market orders carry higher slippage risk but ensure immediate execution. Limit orders provide price control but introduce the risk of missed opportunities. Aligning order types with market conditions, liquidity, and individual goals enhances overall performance. Experienced traders often combine market and limit orders to balance speed, cost, and control. Strategic application considers spread, trading fees, and market depth, making order selection an essential component of professional spot trading. The following table summarises the key distinctions:
| Aspect | Market Orders | Limit Orders |
| Execution Speed | Instant | Conditional |
| Price Control | None | Full control |
| Slippage Risk | Higher | Minimal |
| Liquidity Role | Consumes liquidity | Provides liquidity |
| Best Use Case | Urgent entry or exit | Planned entry or exit |
Additionally, traders use bullet point strategies to maximise order efficiency:
- Execute market orders on high-liquidity pairs to minimise slippage.
- Set limit orders at logical support or resistance levels for precision.
- Monitor order book depth before placing large market orders.
- Adjust limit orders according to anticipated market movements.
- Combine both order types in a single trade to dynamically manage risk.
Executing Market and Limit Orders Effectively on Zoomex
A high-performance trading engine enhances order execution accuracy, critical in volatile spot markets. Deep liquidity ensures minimal slippage when using market orders. Transparent order books allow precise limit order placement, improving strategy efficiency. Low-latency interfaces enable rapid decision-making, enabling timely entries and exits. Security and reliability are essential for confident order execution, ensuring that funds remain protected during trading. Spot Trading on zoomex.com offers these advantages, providing both beginners and professional traders with a seamless experience. By integrating a robust matching engine, multi-layered security, and a user-first approach, traders can focus on strategy execution without operational distractions.
Conclusion
Market orders and limit orders serve distinct purposes in spot trading. Market orders prioritise speed and guaranteed execution but sacrifice control over price, while limit orders offer precision at the expense of execution certainty. Neither order type is universally superior, and their effectiveness depends on individual trading objectives and market conditions. Mastery comes from understanding execution mechanics, evaluating liquidity, and aligning order choice with strategic goals. By integrating market and limiting orders thoughtfully, traders can achieve disciplined execution, minimise risk, and enhance overall performance in spot markets. Success requires ongoing learning, observation of price action, and an appreciation for the nuanced interplay between speed, price control, and risk management.






