Operator Functions in Python
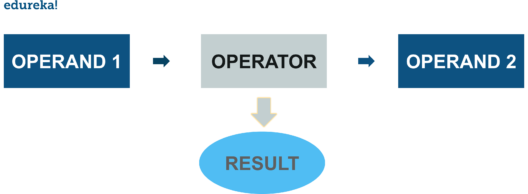
Python has predefined functions for several mathematical, logical, relational, bit wise etc operations under the module “operator”. a number of the essential functions are covered during this article.
- add (a, b) : This function returns additionof the given arguments.
Operation – a + b. - sub (a, b):This function returns difference of the given arguments.
Operation – a – b. - mul (a, b): This function returns productof the given arguments.
Operation – a * b
Output:
4. true div(a,b) :- This function returns division of the given arguments.
Operation – a / b.
5. floor div(a,b) :- This function also returns division of the given arguments. But the value is floored value i.e. returns greatest small integer.
Operation – a // b.
6. pow(a,b) :- This function returns exponentiation of the given arguments.
Operation – a ** b.
7. mod(a,b) :- This function returns modulus of the given arguments.
Operation – a % b.
Output:
8. lt(a, b) :- This function is used to check if a is less than b or not. Returns true if a is less than b, else returns false.
Operation – a < b.
9. le(a, b) :- This function is used to check if a is less than or equal to b or not. Returns true if a is less than or equal to b, else returns false.
Operation – a <= b.
10. eq(a, b) :- This function is used to check if a is equal to b or not. Returns true if a is equal to b, else returns false.
Operation – a == b.
Output:
11. gt(a,b) :- This function is used to check if a is greater than b or not. Returns true if a is greater than b, else returns false.
Operation – a > b.
12. ge(a,b) :- This function is used to check if a is greater than or equal to b or not. Returns true if a is greater than or equal to b, else returns false.
Operation – a >= b.
13. ne(a,b) :- This function is used to check if a is not equal to b or is equal. Returns true if a is not equal to b, else returns false.
Operation – a != b.