Who does not want a smooth home internet? Most of us like things being simple. This means that we may want to avoid complex network terminologies until there is no other way out. The internet today has much more to offer than it had a decade ago. There are different types of internet connection types and a wide range of providers and plans available. So, the options are countless. This gives us more authority as a user to pick the internet type, provider, and plan that fits our connectivity needs the best. For some, cable internet like Charter Spectrum is a winner while others might be attracted to a more basic network type like DSL internet to suffice their connectivity needs. DSL is a more common type of internet technology easily found in the market. As evident by the name, DSL or Digital Subscriber Line is a wired internet connection that makes use of the phone lines to transmit internet signals. If you want to know more about a DSL connection, then here we have gathered every bit of essential information that can be of use if you are thinking of getting a DSL internet connection. So, dive in and get to know all about it:
DSL and Dial-Up – Don’t Mix Them Up!
Now, most of us might recall the earliest form of internet connection, which used phone lines to connect to the internet by establishing a dial-up connection. Since DSL also uses copper phone wires to transfer internet connectivity, it is often confused with a dial-up connection. This is not true. A dial-up connection uses data packets comprising low-frequency bands, whereas a DSL connection uses high-frequency bands to transmit data. While establishing a dial-up connection, the telephone line is disconnected but this does not happen during a DSL connection. This means that the phone service stays on when you load web pages.
Parts of a DSL Connection
A DSL internet service provider has a decoding device called DSLAM, also known as the Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer. It is responsible for communicating with the internet backbone and establishing a connection between the ISP and the subscribers.
This internet backbone is usually comprised of fiber technology and is capable of allowing higher bandwidth transmission. The data is sent over the internet backbone and then eventually reaches the homes of customers. Copper cables carry the data signals just before they reach the subscribers.
So, if we are to summarize the various components of a DSL connection, here is how it works:
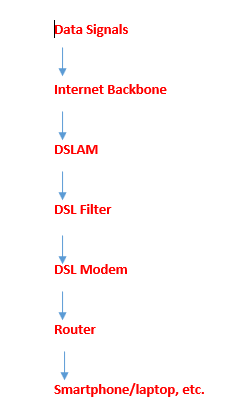
DSL Speed
As compared to other internet types, DSL internet offers a more moderate but consistent speed. Therefore, if you are looking for blazing fast internet speeds, you can prefer cable or fiber internet. However, if you seek average internet speeds that suffice your online routine, then a DSL connection will be the right fit for you. Those who live in rural areas should probably opt for a DSL connection, which is an ideal solution for catering to their connectivity needs.
The average DSL internet speed might be around 6 Mbps while cable internet offers an average speed of nearly 100 Mbps. With a 6 Mbps internet speed, you can easily browse the web, send emails, shop online, and do video conferencing smoothly. However, if you want multiplayer gaming and love to stream in 4K, you must subscribe to a DSL plan that ensures a speed of at least 25 Mbps. If not available, in that case, you should rather prefer a cable or fiber internet plan to fulfill your excessive streaming or gaming needs.
DSL internet has 100% availability throughout the US that makes it a convenient connectivity option.
Types of DSL Connections
DSL internet has around ten subtypes available in the market. Amongst them, two of the most popular ones include VDSL and ADSL.
-
VDSL
It stands for Very High Bit Rate Digital Subscriber Line and can transfer data at around 12 MHz frequency, thereby making download speeds as high as 300 Mbps possible.
-
ADSL
It stands for Asynchronous Digital Subscriber Line and provides a higher download speed and a much lower upload speed. The latest version, ADSL2+ can transmit data at a frequency of 2.2 MHz band, offering download speeds up to 15 Mbps while upload speeds of 3 Mbps.
Cost
The installation cost of DSL is considerably low as compared to any other internet type. Therefore, if you are looking for more budget-friendly internet connectivity, then DSL internet is a very promising choice to make.
Final Words
DSL is indeed one of the most common internet types with 100% coverage across the US. It is more affordable, consistent, and has a lower installation cost. It is an ideal choice for users dwelling in rural areas and offers a satisfactory moderate speed at a lower cost.