AngularJS Input Email
- input [email] is one of the input directive in module ng.
- To validate an email address means to check the email address is valid email or not.
- It is used to text input with email validation. If it is not a valid email address means sets the email validation error key.
Syntax for input [email] directive in AngularJs:
<input type="email"
ng-model="string"
[name="string"]
[required ="string"]
[ng-required="string"]
[ng-minlength="number"]
[ng-maxlength="number"]
[pattern ="string"]
[ng-pattern ="string"]
[ng-change ="string"]>Parameter Values:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| ngModel | Defines angular expression to data-bind to. |
| name (optional) | Name of the form under which the control is available. |
| required(optional) | If the value is not entered then sets the required validation error key. |
| ngRequired (optional) | Sets the required attribute and required validation to the element when the ngRequired expression evaluates true. Instead of required use ngRequired when we want to data-bind to the required attribute. |
| ngMinlength (optional) | States the minlength validation error key if the value is shorter than minlength. |
| ngMaxlength (optional) | States the maxlength validation error key if the value is longer than maxlength. |
| pattern(optional) | It is similar to ngPattern except that the attribute value is the actual string. It contains the regular expression body that will be converted to a regular expression as in the ngPattern directive. |
| ngPattern (optional) | States pattern validation error key if the ng model value does not match RegExp found by evaluating the Angular expression given in the attribute value. If the expression evaluates to a RegExp object, then this is used directly. If the expression evaluates to a string, then it will be converted to a RegExp after wrapping it in ^ and $ characters. For instance, "abc" will be converted to new RegExp ('^abc$'). |
| ngChange (optional) | An expression of Angular to be executed when input changes due to user interaction with the input element. |
Sample coding for input[email] directive in AngularJS
Tryit<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Wikitechy AngularJS Tutorials</title>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.5.6/
angular.min.js"> </script>
</head>
<body>
<form ng-app="myApp" name="Form" ng-controller="emailCtrl">
<h3>input[email] directive example</h3>
Email:
<input type="email" name="input" ng-model="emailtext" required>
<span ng-show="Form.input.$error.required">
Required!</span>
<span ng-show="Form.input.$error.email">
Not a valid email!</span>
<p>text = {{emailtext}}</p>
<p>Form.input.$valid = {{ Form.input.$valid }}</p>
<p>Form.input.$error = {{ Form.input.$error }}</p>
<p>Form.$valid = {{Form.$valid}}</p>
<p>Form.$error.required = {{!!Form.$error.required}}</p>
<p>Form.$error.email = {{ !!Form.$error.email }}</p>
</form>
<script>
var app = angular.module("myApp", []);
app.controller('emailCtrl',function($scope) {
}]);
</script>
</body>
</html>Code Explanation input[email] directive in AngularJS:

- The ng-app specifies the root element (“myapp”) to define AngularJS application.
- Declare the form name as “form”.
- ng-controller specifies the application controller in AngularJS the controller value is given as “emailCtrl”.
- Here we declare the input type name as “input”.
- The ng-model bind an input field value to AngularJS application variable (“emailtext”).
- ng-show directive is used to hides HTML elements. If the required directive shows an error the content is displayed like “Required”
- ng-show directive is used to hides HTML elements. If the required directive shows an error the content is displayed like “Not valid email”
- The expression (emailtext) to check whether the valid text or not. If the text is not valid and the output will not updated any text in the <p> tag. otherwise the text is updated.
- Form.input.$valid to checks the valid email or not and the output will be displayed in <p> tag.<
- Form.input.$error to check whether the email is error or not .If the email is in error it through the exception (Like “required”=”true) otherwise it is an empty curly braces ( { } ).
- Form.$valid is used to check whether the form is valid or not and output will be displayed in <p> tag.
- Form.error.$required is used to email is required or not. If the email is required and output will be displayed as false otherwise true.
- Form.error.$email is used to check whether the email is error or not and output will be displayed in the <p> tag.
Sample Output input [datetime-local] directive in AngularJS:
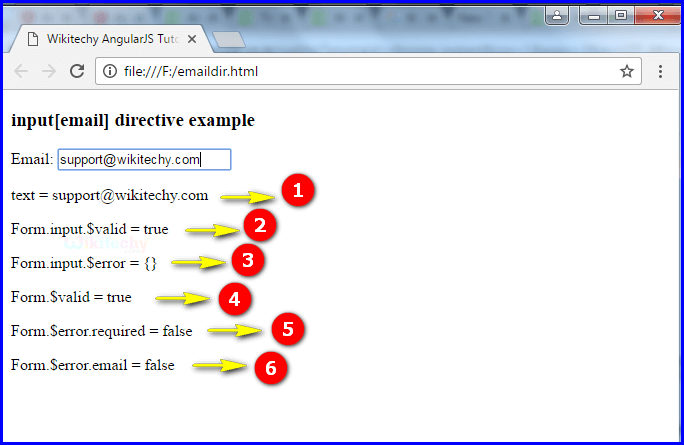
- When user type the text in input field and the output will be displays as [email protected].
- The output displays true because it is consider as a valid email.
- The output displays empty curly braces there is no error in the email.
- The output displays true it is valid mail.
- If the text box is not an empty so the output displays as false.
- If the email is correct ([email protected]) so the output will displays false.
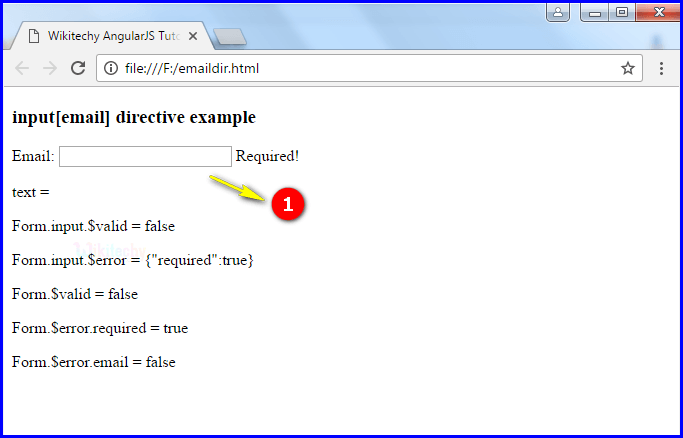
- If user does not type any text in the input field and output displays as “Required”.

- If the user does not type a valid mail in the text field and output displays like “Not valid email!”
Tips and Notes
- The input [email] uses a regular expression to validate email addresses. If we need exact validation, you can use ng-pattern or Modify the in-built validators.
