C# Class | C# Object and Class - c# - c# tutorial - c# net
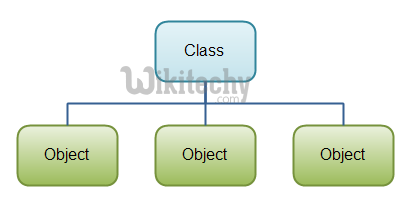
C# Class
C# Object
- In C#, Object is a real world entity, for example, chair, car, pen, mobile, laptop etc.
- In other words, object is an entity that has state and behavior. Here, state means data and behavior means functionality.
- Object is a runtime entity, it is created at runtime.
- Object is an instance of a class. All the members of the class can be accessed through object.
- C# is an object-oriented language, program is designed using objects and classes in C#.
- Let's see an example to create object using new keyword.
Class and Object
Syntax:
Student s1 = new Student();//creating an object of Student - In this example, Student is the type and s1 is the reference variable that refers to the instance of Student class. The new keyword allocates memory at runtime.
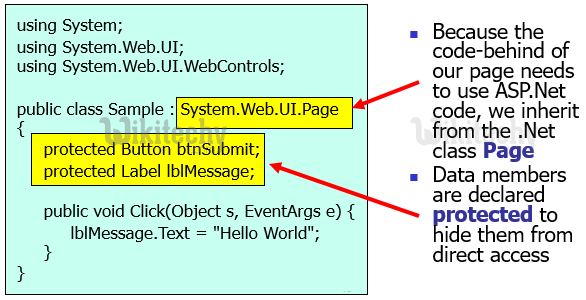
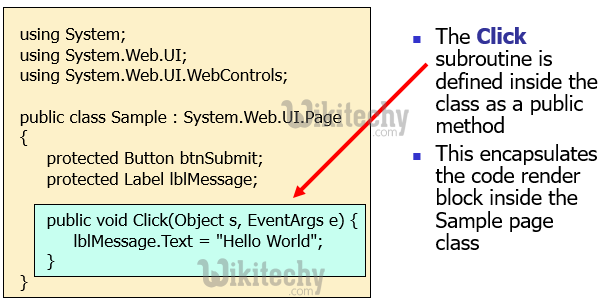
C# Code Behind files
- Splits visual design from functional development
- This allows code developers to work separately from presentational designers
- Code render blocks are placed in a separate C#, .cs file
- This prevents "spaghetti" code and helps make pages more understandable
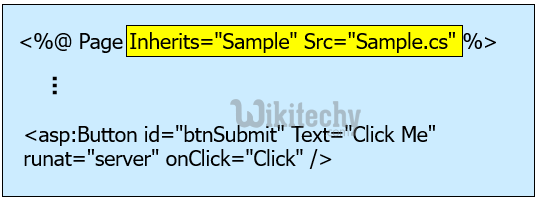
C# web pages - Code Behind files
- sample.aspx contains page layout and static content
- sample.aspx inherits from the class Sample
- The definition of class Sample is in the Sample.cs file
C# Class
- In C#, class is a group of similar objects. It is a template from which objects are created. It can have fields, methods, constructors etc.
- A class is a construct that defines a collection of properties and methods in a single unit, which does not change during the execution of a program.
- Let's see an example of C# class that has two fields only.

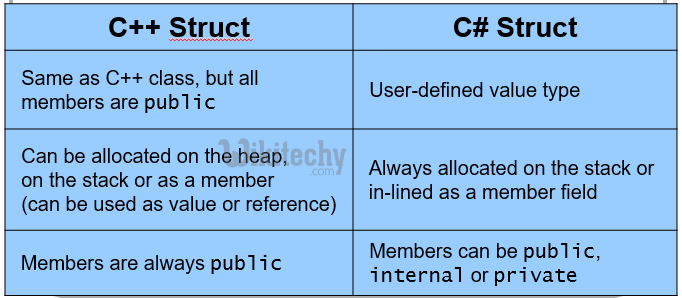
c# class vs struct :
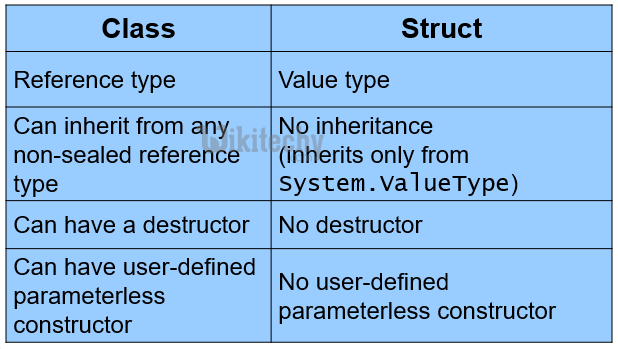
c# struct vs c++ struct :
Syntax:
public class Student
{
int id;//field or data member
String name;//field or data member
} 
C# Object and Class Example
- Let's see an example of class that has two fields: id and name. It creates instance of the class, initializes the object and prints the object value.
using System;
public class Student
{
int id;//data member (also instance variable)
String name;//data member(also instance variable)
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student s1 = new Student();//creating an object of Student
s1.id = 101;
s1.name = "Sonoo Jaiswal";
Console.WriteLine(s1.id);
Console.WriteLine(s1.name);
}
}
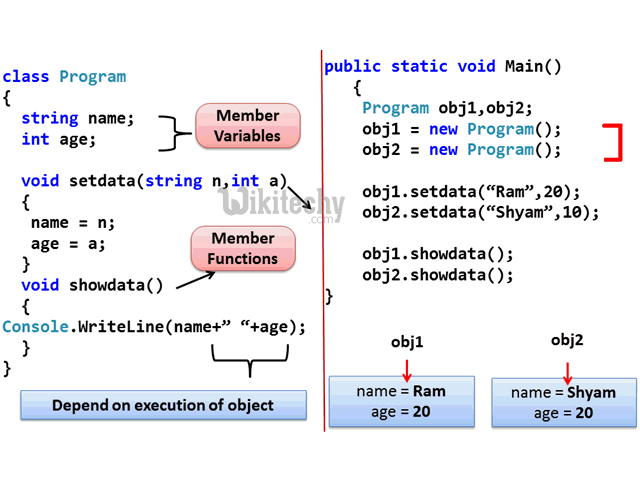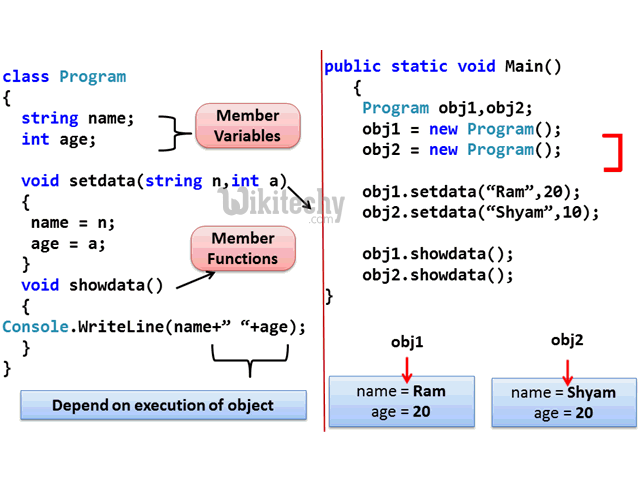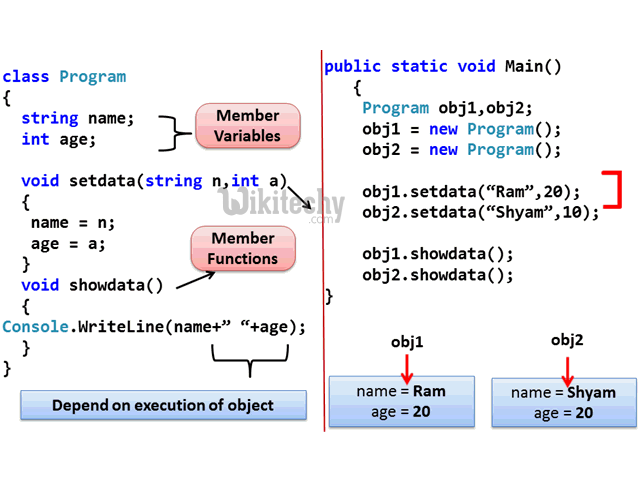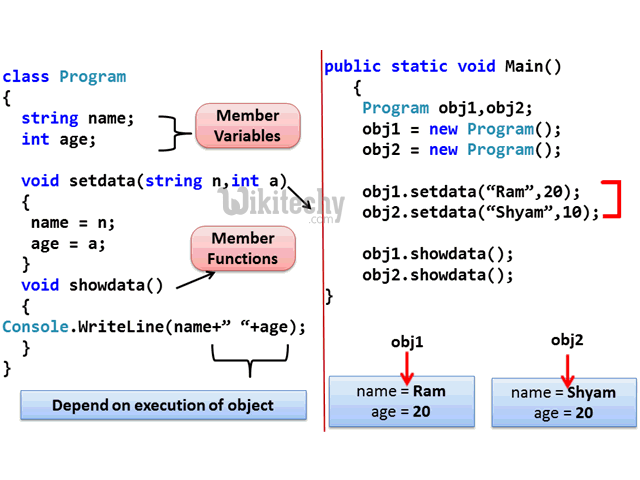
Class and Object
C# examples - Output :
101
Sonoo Jaiswal
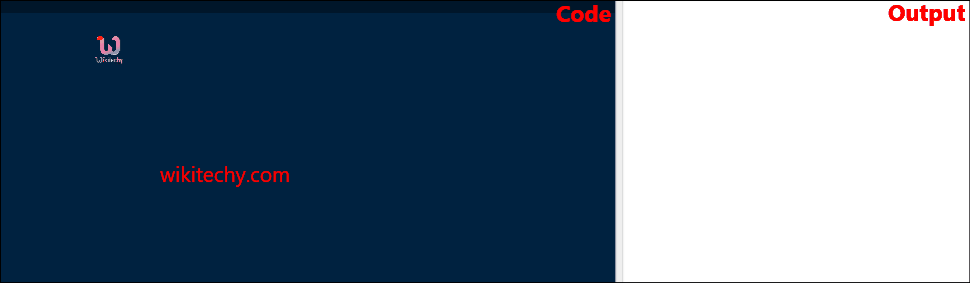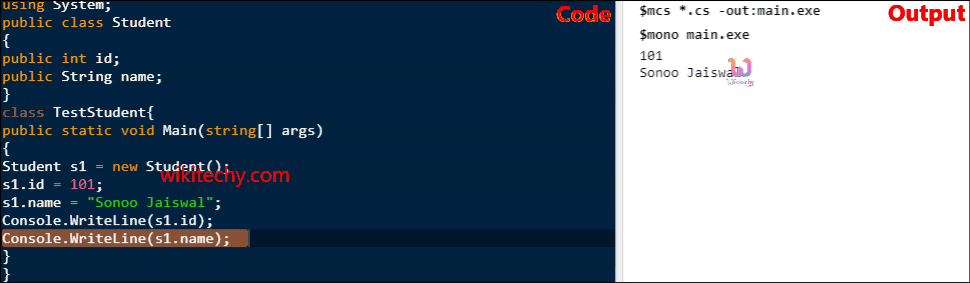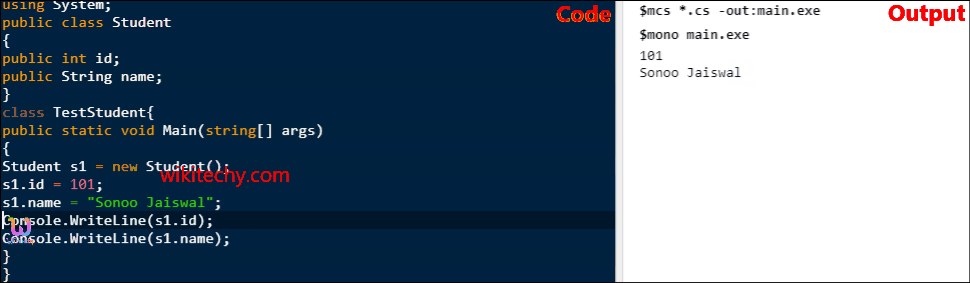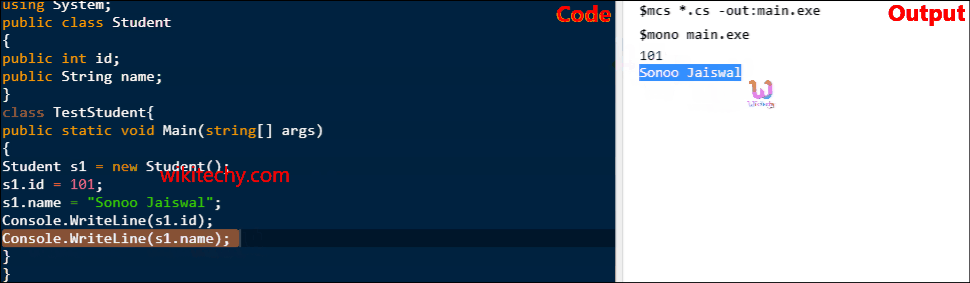
C# Class Example 2: Having Main() in another class
- Let's see another example of class where we are having Main() method in another class. In such case, class must be public.
using System;
public class Student
{
public int id;
public String name;
}
class TestStudent{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.id = 101;
s1.name = "Sonoo Jaiswal";
Console.WriteLine(s1.id);
Console.WriteLine(s1.name);
}
} C# examples - Output :
101
Sonoo Jaiswal
C# Class Example 3: Initialize and Display data through method
- Let's see another example of C# class where we are initializing and displaying object through method.
using System;
public class Student
{
public int id;
public String name;
public void insert(int i, String n)
{
id = i;
name = n;
}
public void display()
{
Console.WriteLine(id + " " + name);
}
}
class TestStudent{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student s1 = new Student();
Student s2 = new Student();
s1.insert(101, "Ajeet");
s2.insert(102, "Tom");
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}
C# examples - Output :
101 Ajeet
102 Tom
C# Class Example 4: Store and Display Employee Information
using System;
public class Employee
{
public int id;
public String name;
public float salary;
public void insert(int i, String n,float s)
{
id = i;
name = n;
salary = s;
}
public void display()
{
Console.WriteLine(id + " " + name+" "+salary);
}
}
class TestEmployee{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Employee e1 = new Employee();
Employee e2 = new Employee();
e1.insert(101, "Sonoo",890000f);
e2.insert(102, "Mahesh", 490000f);
e1.display();
e2.display();
}
}
C# examples - Output :
19Y4NSiG8kkzwWjMD17euEaQ5PErpwxWkPc# Access Modifiers :
- public is the most common access specifier in C# .
- It can be access from anywhere, that means there is no restriction on accessibility.
- The scope of the accessibility is inside class as well as outside.
- The type or member can be accessed by any other code in the same assembly or another assembly that references it.
- The scope of the accessibility is limited only inside the classes or struct in which they are declared.
- The private members cannot be accessed outside the class and it is the least permissive access level.
- The scope of accessibility is limited within the class or struct and the class derived (Inherited )from this class.
- The internal access modifiers can access within the program that contain its declarations and also access within the same assembly level but not from another assembly.
- Protected internal is the same access levels of both protected and internal.
- It can access anywhere in the same assembly and in the same class also the classes inherited from the same class .
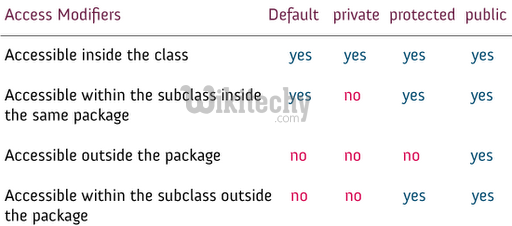
c# access specifiers
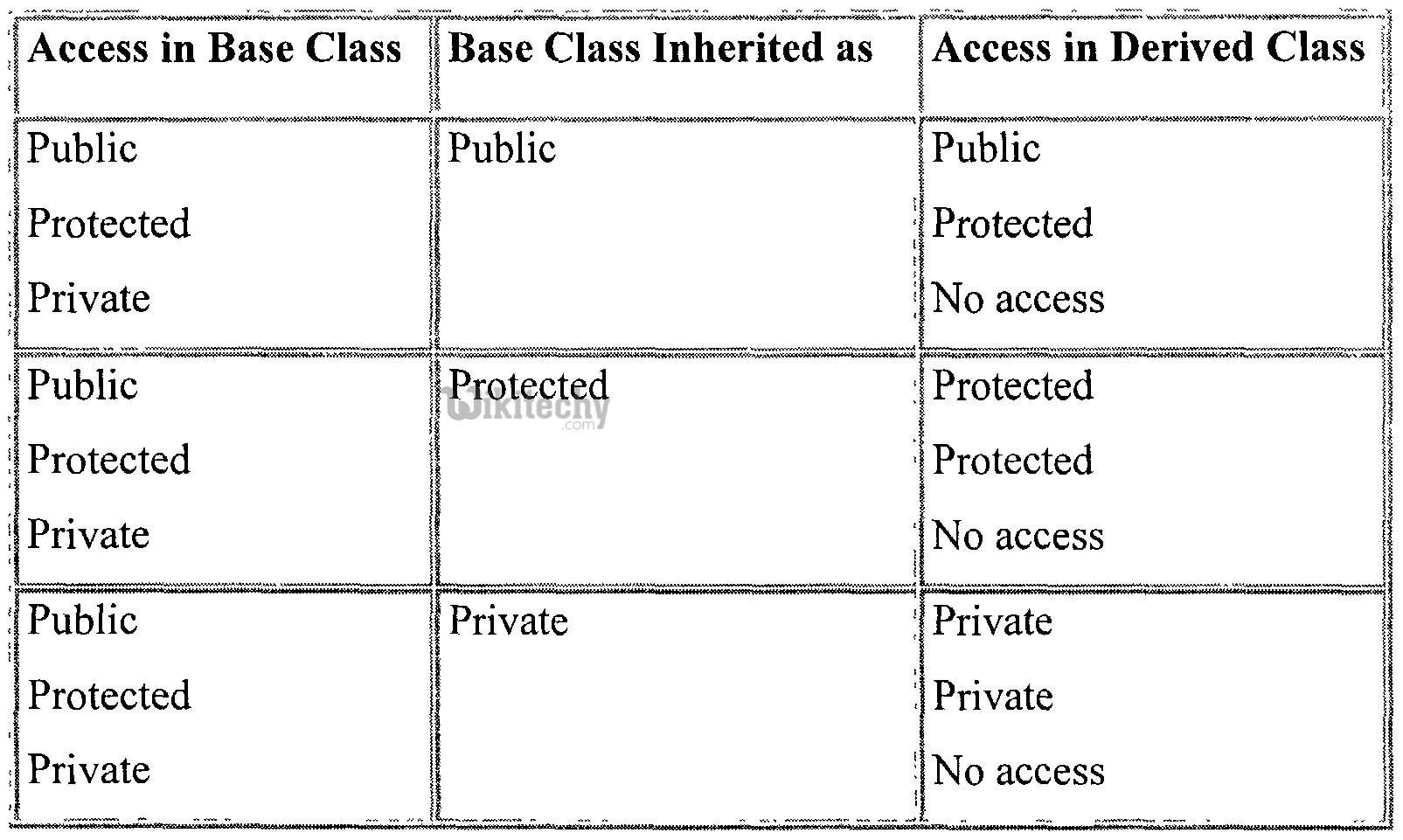
c# public protected private access specifiers
